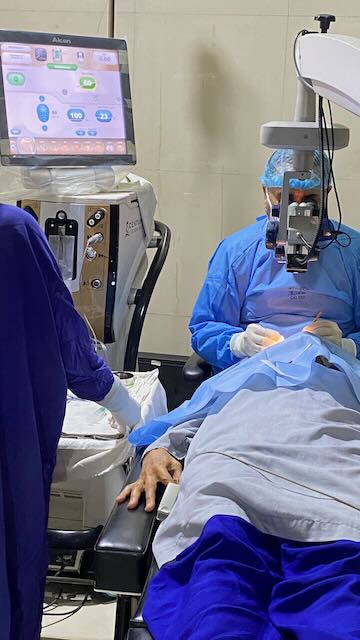
Phacoemulsification is a modern surgical technique for removing cataracts from the eye. It is also known as “phaco” for short. This method involves a metal tip Vibrating at a very high-frequency (ultrasound waves), to break up the cataract into small pieces, which are then suctioned out of the eye. Phacoemulsification has become the standard of care for cataract surgery and is widely regarded as a safe and effective procedure.
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, which means that the patient is awake but does not feel any pain. A small incision is made in the cornea, the clear front part of the eye, and a tiny probe is inserted into the eye. This probe emits high-frequency sound waves that break up the cataract into small pieces that can be easily removed from the eye.
One of the main advantages of phacoemulsification is that it requires a very small incision, typically less than 3 millimeters in diameter. This means that there is less trauma to the eye, which leads to faster healing and fewer complications. The small incision also allows for faster visual recovery, as the eye does not need to heal as much after the procedure.
Phacoemulsification can also be performed using a variety of different techniques and instruments, depending on the type of cataract and the surgeon’s preference. For example, some surgeons may use a “divide and conquer” technique, which involves dividing the cataract into four quadrants and removing each quadrant separately. Others may use a “chop” technique, which involves breaking up the cataract into smaller pieces and removing them individually.
Overall, phacoemulsification is a safe and effective procedure for removing cataracts and restoring vision. It has revolutionized cataract surgery and is now considered the gold standard for the procedure. Patients undergoing phacoemulsification can expect a quick and relatively painless recovery and enjoy improved vision and quality of life after the procedure.
Dr Sarbjit Singh
